If Poland's borders had not been changed after World War II, the 100th anniversary of the Polish Red Cross would be celebrated with the Lviv, Volhynian, and Wilno branches, which still operate today but under the structures of different state associations.
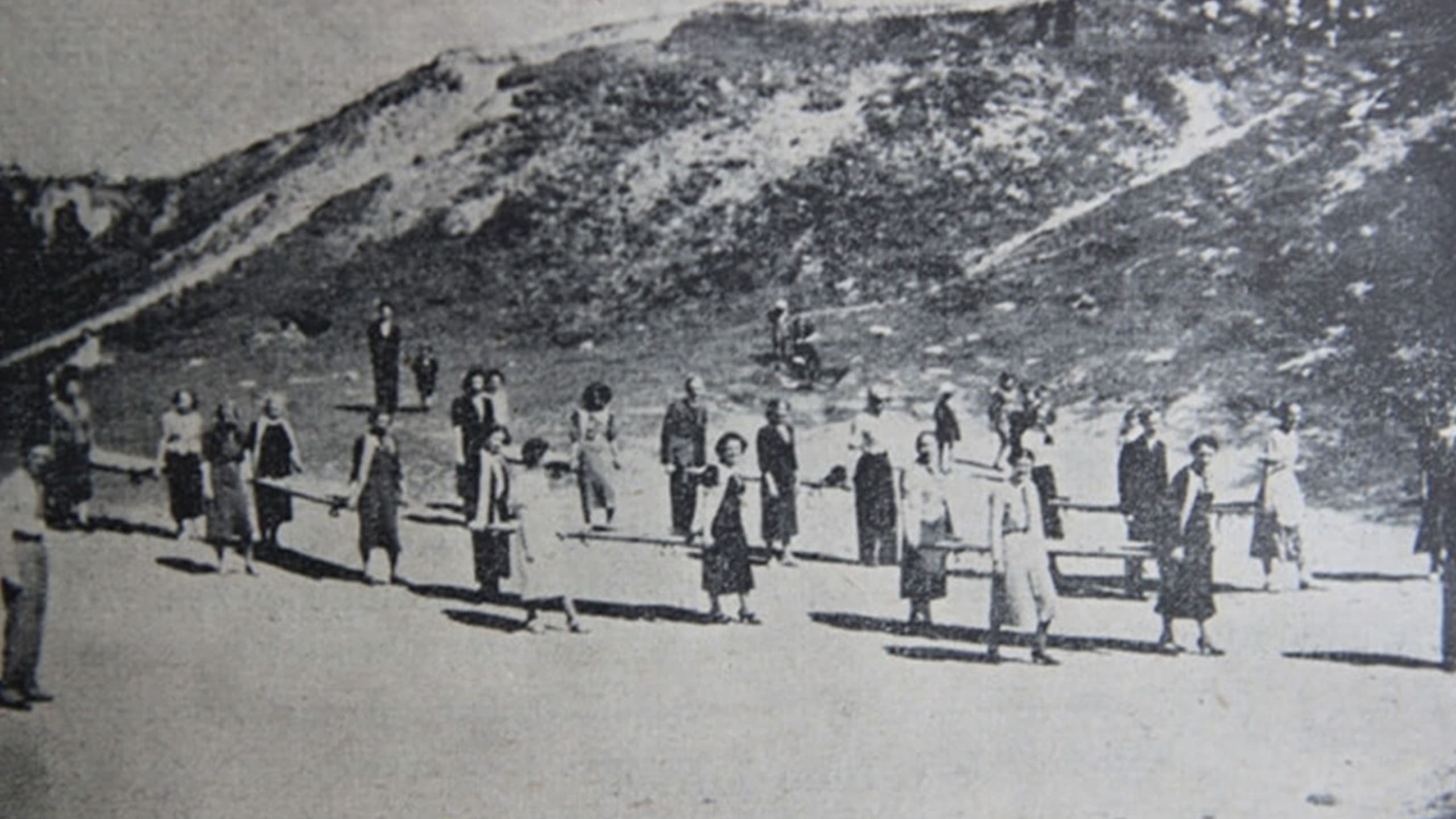

After the establishment of the Polish Red Cross Society, 4 large District Committees were formed: Małopolski, Wielkopolski, South-Eastern, and Polesko-Miński, with main centers in Kraków, Lviv, Poznań, and Warsaw. The creation of these districts was recorded in the first PTCK Statute from 1919. Thanks to the intensive work of the members of the district committees, new field branches were opened every year. Thus, soon a branch was established in Łuck (Volyn District), and in 1925 in Vilnius (Vilnius District). These units conducted active Red Cross activities: they operated sanatoria (Lviv), general and dental outpatient clinics (Lviv, Łuck), and radiation therapy offices (Lviv). Weeks of the Red Cross were organized, rescue teams operated, and youth circles' activities were developed.




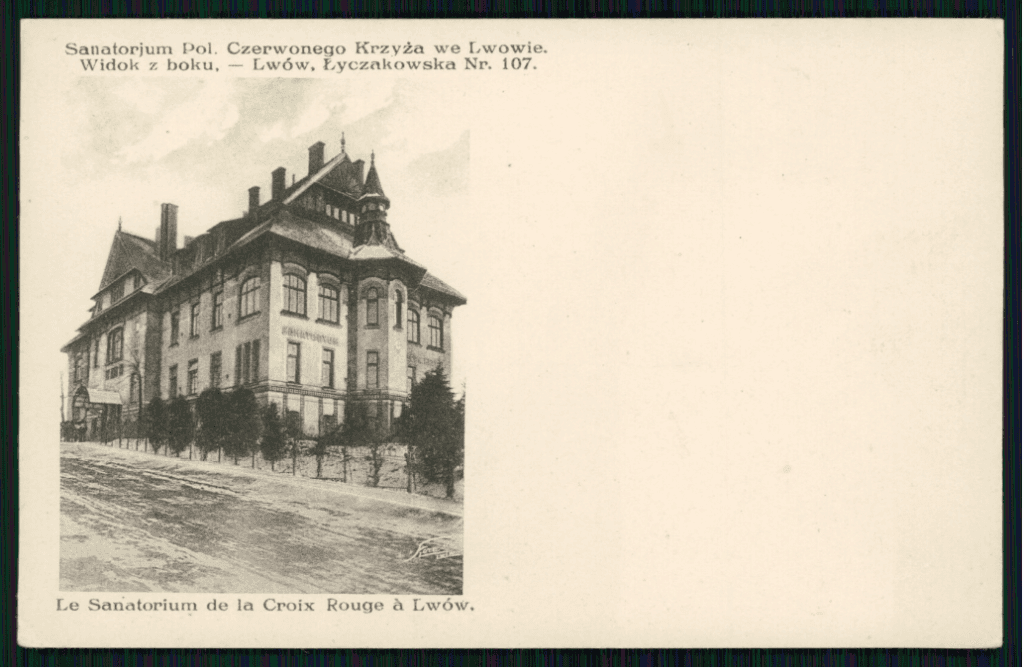



The branch in Lviv regularly provided transect treatment for children and organized rescue road posts that were responsible for providing first aid to road accident victims and training drivers in the area of first aid. The branches conducted day rooms for children and youth, organized fundraising for the poorest. Various health and social campaigns were regularly carried out, often surprising to us today, such as the disinfection of telephone devices. The aim of the campaign was to keep telephone devices 'in a state ensuring public health.' Citizens could report public and private devices for disinfection, which was carried out for a fee by employees of the Lviv Red Cross branch using a special disinfectant. The funds obtained in this way were allocated for training purposes of the volunteer health service of the Red Cross and the maintenance of sanitary equipment. Another source of funding for activities was the sale of first aid kits. The highest demand was for 'tourist-excursion', 'suitcase', and 'cabinet-wall' first aid kits. An important task of the branches was to create and train a volunteer health service as an auxiliary body of the military sanitary service in case of war. The branches in Lviv, Vilnius, and Łuck operated within the structures of the Red Cross until World War II.
Facts about the Polish Red Cross
Only after the fourth request to the International Red Cross was the Polish Red Cross recognized on the international stage.
The beginnings of blood donation in the Red Cross date back to 1935, which took place 83 years ago.
If the borders of Poland had not been changed after World War II, the 100th anniversary of the Polish Red Cross (PCK) would have been celebrated with the Lviv, Volhynian, and Wilno branches, which are still active today but under the structures of different state associations.
The employees of the Polish Red Cross carried out the exhumation of Polish officers murdered in the Katyn Forest while also being responsible for creating the official Katyn Lists
The Red Cross movement and its foundations were the source for the establishment of sanitary services for wounded soldiers under the names Polish White Cross and Polish Green Cross.
Over the years, the rules for statutory financing of the PCK's activities have changed, as has our role and position within the state.
The PCK enjoyed immense public trust during the Second Polish Republic, and the most important figures in the state always spoke about our organization with the utmost respect.
To this day, in Tarnów, Małopolska, there is a nearly 100-year tradition of parades through the city organized on the occasion of the Polish Red Cross Week.
On February 8, 2018, it was 50 years since the establishment of the badge of the Honorable Blood Donor
On February 8, 2018, it marked 50 years since the establishment of the badge of the Meritorious Honorary Blood Donor
PCK never accepted any gratifications and did not support the Nazi authorities, thereby exposing itself to severe consequences.
The Polish Red Cross was the initiator of healthcare in rural areas during the interwar period and the establishment of the first village health centers.
PCK was involved in the construction of the Marshal Piłsudski Mound in Sowińca in Krakow in 1936
At the beginning of 1919, within the structures of the newly established Polish Red Cross Society, 3 District Branches of the PTCK were created: for Galicia, the Grand Duchy of Posen, and Silesia.
During its 100-year activity, the Polish Red Cross, the International Committee of the Red Cross, honored 102 Polish nurses associated with our organization with the Florence Nightingale Medal.
The Polish Red Cross was the organizer of parachuting courses
Did two Polish doctors working at the Red Cross hospital during World War II save more lives than Oskar Schindler?
There existed simultaneously the Polish Red Cross and the Polish White Cross, whose president was Helena Paderewska.
There was a time in the history of PCK when, legally, two or even three Main Boards of PCK operated simultaneously.
Help us endlessly
Thanks to the kindness and support of our Donors, we can help children, seniors, support medical rescuers, promote the idea of blood donation, and implement many other projects that save lives in times of conflict or humanitarian crises. Every donation and every form of support is significant because the Polish Red Cross connects those in need with those who want to provide help. Let’s help together!
See also
19. The PCK employees conducted the exhumation of Polish officers murdered in the Katyn Forest while also being responsible for creating the official Katyn Lists.
After the Red Army entered Polish territory, thousands of Polish soldiers and representatives of the intelligentsia were taken into Soviet captivity. The NKVD placed them in special camps, having previously organized a selection for officers, non-commissioned officers, and privates.
Only after the fourth request to the International Red Cross was the Polish Red Cross organization recognized on the international stage.
The first time such a proposal was made was on August 5, 1915, by the Polish Committee for Sanitary Aid, which wanted to be recognized by the International Committee of the Red Cross as a national association in the reborn Poland, presenting its activities in a comprehensive memorandum.
You are currently viewing a page filtered by content from the department. Cała PolskaIf you want to view content from Cała Polskaclick the button